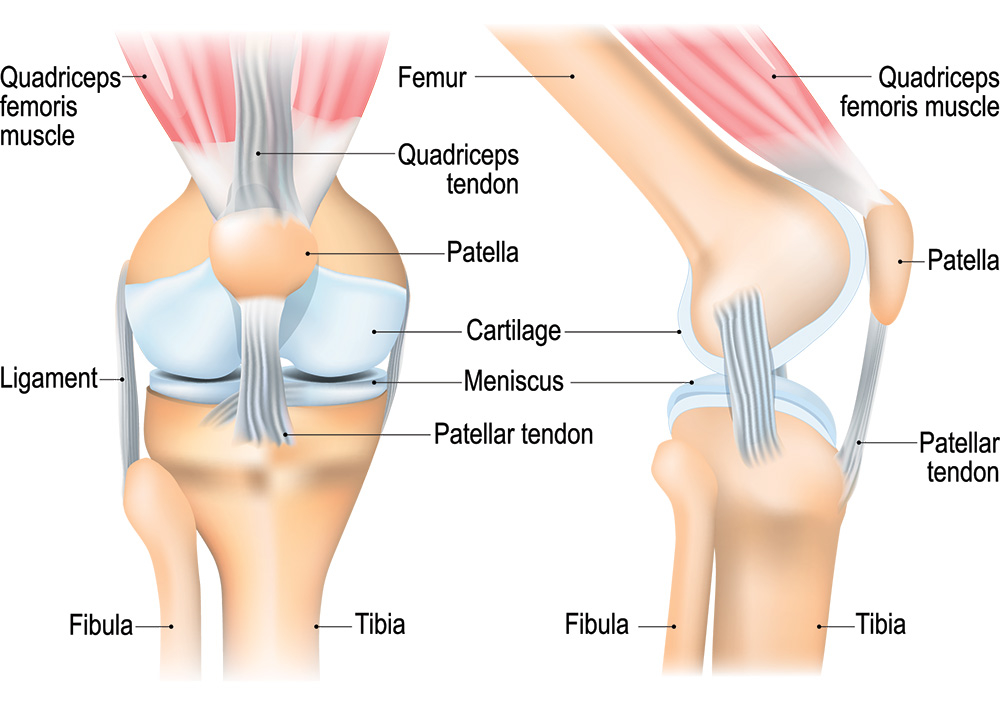
Knee Injury
Types of Knee Injuries and Their Treatments
1. Knee Strains and Sprains
- Description: Overstretching or tearing of muscles (strains) or ligaments (sprains) around the knee.
- Treatment:
- Rest: Avoid activities that cause pain.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression: Use elastic bandages to minimize swelling.
- Elevation: Elevate the knee to reduce swelling.
- Medications: NSAIDs for pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee.
2. Ligament Injuries (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL)
- Description: Tears or sprains of the knee ligaments. The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) and MCL (medial collateral ligament) are most commonly injured.
- Treatment:
- Rest and Immobilization: Use of braces or crutches.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and stability.
- Medications: NSAIDs for pain and inflammation.
- Surgery: In severe cases, such as a complete tear, reconstructive surgery may be needed, especially for active individuals.
3. Meniscus Tears
- Description: Tears in the meniscus, the cartilage that acts as a cushion between the thigh bone and shin bone.
- Treatment:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the injury.
- Ice: Apply ice to reduce swelling and pain.
- Medications: NSAIDs for pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and range-of-motion exercises.
- Surgery: Arthroscopic surgery to repair or remove the torn part of the meniscus if conservative treatments fail.
4. Knee Fractures
- Description: Breaks in the bones of the knee, such as the patella (kneecap).
- Treatment:
- Immobilization: Use of casts or braces to keep the bone in place while it heals.
- Surgery: May be necessary to align and stabilize the bones using screws, plates, or rods.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy to restore function and strength after the bone has healed.
- Medications: Pain relief and possibly medications to aid bone healing.
5. Dislocation
- Description: The knee bones are forced out of alignment.
- Treatment:
- Reduction: A procedure to put the knee back in place, performed by a medical professional.
- Immobilization: Use of a brace or splint.
- Physical Therapy: To restore movement and strengthen the knee.
- Surgery: May be required in cases of recurrent dislocation or associated injuries.
6. Tendon Injuries
- Description: Tears or inflammation of the tendons, such as the patellar tendon.
- Treatment:
- Rest: Avoid activities that cause pain.
- Ice: Apply ice to reduce swelling and pain.
- Medications: NSAIDs for pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and flexibility exercises.
- Surgery: In severe cases, such as a complete tear, surgical repair may be needed.
General Treatment Approaches
- RICE Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation to manage initial injury symptoms.
- Medications: NSAIDs to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Supportive Devices: Use of braces, crutches, or knee supports to aid recovery.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate the injury and gradually returning to normal activities.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe pain or swelling.
- Inability to move the knee or bear weight.
- Symptoms of infection, such as fever or redness around the knee.
- Persistent pain that does not improve with home treatment.
Prevention Tips
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on the knee joints.
- Exercise Regularly: Focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee and improving flexibility.
- Use Proper Techniques: When lifting heavy objects or during physical activities.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Supports the knees and reduces impact.
- Warm-Up and Cool Down: Properly before and after exercise to prevent injuries.