Cysts in neck
Causes
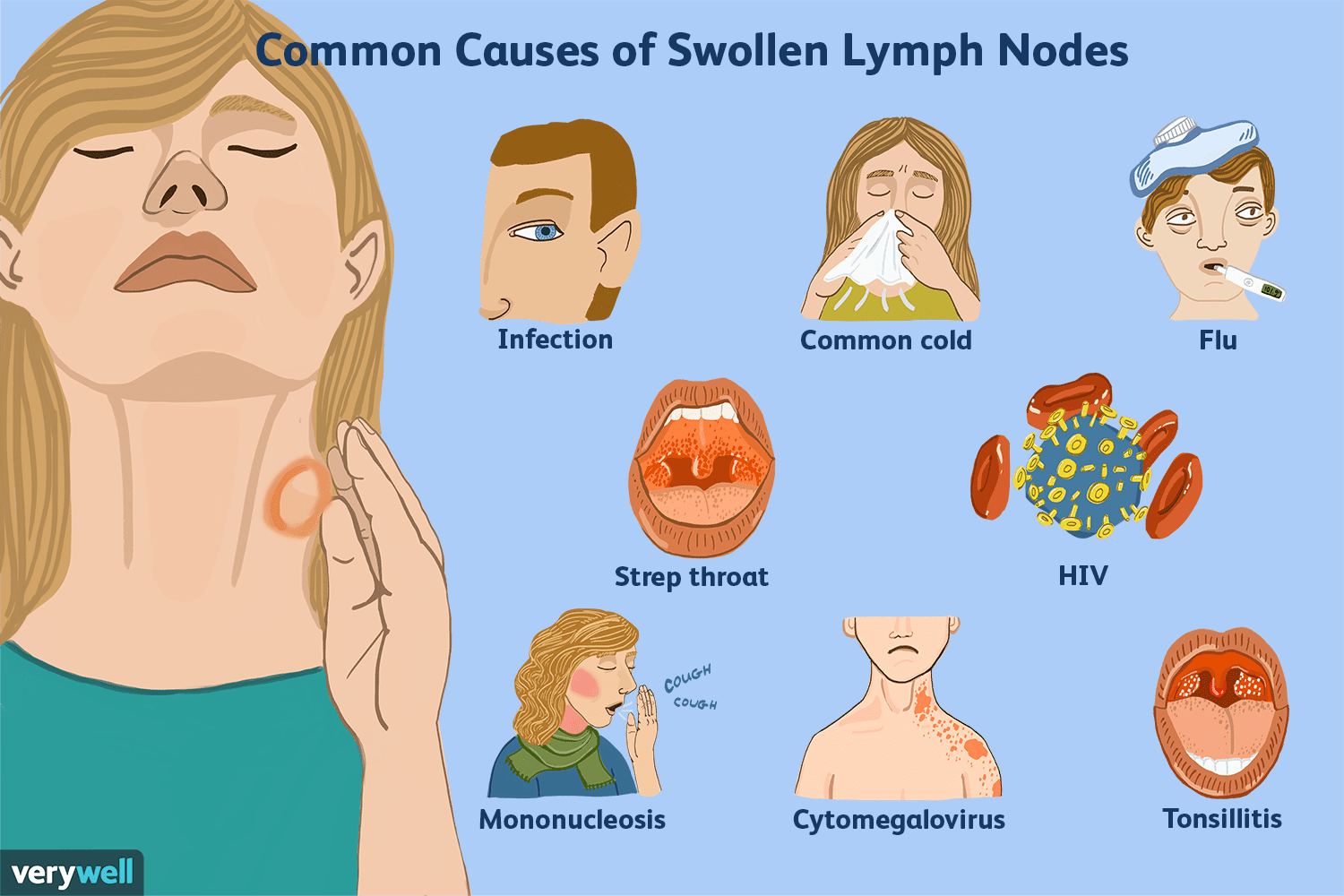
Neck lumps may be caused by systemic disease, such as the following.
- Tumors: Whether cancerous or not, growths in the neck result in neck lumps. The majority of neck lumps are not cancerous and are caused by conditions such as tonsillitis or are cysts or benign lipomas.
- Nodules: Nodules are another form of abnormal growth, typically on the thyroid gland. The thyroid is located just below the Adam’s apple and can show lumps from nodules or cancer.
- Viruses: Cold viruses affect the upper respiratory system, including components of the neck. Lymph nodes can swell as they fight the virus (lymphadenopathy).
Symptoms
If you have a neck lump, it can likely be described by the following.
- Visible mass in the neck
- Mass in the neck detected only by touch (not visible)
- Neck swelling
- Neck tenderness/pain
One of the most important tasks performed by the neck is linking the head to the rest of the body through muscles and vessels. In addition, the neck houses critical components for breathing, speaking and eating. The glands, nodes, and muscles can all develop a lump, and while the lump itself might be noticeable, the underlying cause may not be as clear.
Precautions
Investigations
The first-line investigation for a suspicious neck lump is ultrasound +/- fine needle aspiration (FNA). Ultrasound provides characterisation of lymph nodes, salivary glands, vascular structures, and thyroid nodules. Indeed, ultrasound findings alone can be sufficient to make a diagnosis of certain neck lumps.
Treatment
This treatment involves injecting the cyst with a medicine that reduces swelling and inflammation. Incision and drainage. With this method, your doctor makes a small cut in the cyst and gently squeezes out the contents. This is a fairly quick and easy method, but cysts often recur after this treatment.
Complication
Infection. Cysts can become infected and painful (abscessed). Skin cancer. In very rare cases,