TONSILS
CAUSES
Most cases of tonsillitis are caused by a viral infection, such as the viruses that cause the common cold or flu virus (influenza). Some cases can also be caused by a bacterial infection, typically a strain of bacteria called group A streptococcus bacteria
Symptoms
Tonsillitis most commonly affects children between preschool ages and the midteenage years. Common signs and symptoms of tonsillitis include:
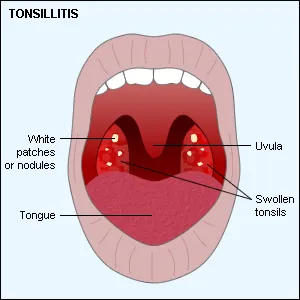
- Red, swollen tonsils
- White or yellow coating or patches on the tonsils
- Sore throat
- Difficult or painful swallowing
- Fever
- Enlarged, tender glands (lymph nodes) in the neck
- A scratchy, muffled or throaty voice
- Bad breath
- Stomachache
- Neck pain or stiff neck
- Headache
Risk factors
Risk factors for tonsillitis include:
- Young age. Tonsillitis most often affects children, and tonsillitis caused by bacteria is most common in children ages 5 to 15.
- Frequent exposure to germs. School-age children are in close contact with their peers and frequently exposed to viruses or bacteria that can cause tonsillitis.
Treatment
- Encourage rest
- Provide adequate fluids
- Prepare a saltwater gargle.
- Offer lozenges.
- Treat pain and fever.
- Avoid irritants
When to see a doctor
It’s important to get an accurate diagnosis if your child has symptoms that may indicate tonsillitis.
Call your doctor if your child is experiencing:
- A sore throat with fever
- A sore throat that doesn’t go away within 24 to 48 hours
- Painful or difficult swallowing
- Extreme weakness, fatigue or fussiness
Get immediate care if your child has any of these signs:
- Difficulty breathing
- Extreme difficulty swallowing
- Excessive drooling